What Is Website Development?
Website development refers to the complete process of building, creating, and maintaining websites. It includes everything from writing markup and coding to managing databases, configuring servers, and developing content management systems (CMS).
In simpler terms, website development covers all the technical and creative work that goes into making a website function smoothly and look appealing to users.
If you’re planning to start a career in web development, a big part of the journey involves learning programming languages. Depending on your focus, you might explore:
-
Front-end languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for designing user interfaces and enhancing the visual experience.
-
Back-end languages like Python, PHP, Java, or Ruby for server-side logic, database integration, and application functionality.
However, mastering programming alone isn’t enough. A successful web developer also needs to understand how the web works — including concepts like hosting, domains, protocols, APIs, and client-server communication. These fundamentals form the backbone of both front-end and back-end development.
Why Is Web Development Important?
In today’s digital-first world, over 5.5 billion people are connected through the internet — using it daily for communication, education, business, and entertainment. This massive online presence has made web development one of the most crucial and fast-growing industries globally.
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for skilled web developers keeps rising. In fact, job opportunities in this field are projected to grow by 8% by 2033, outpacing many other tech careers.
Every organization — from startups to global enterprises — relies on web development to build a strong online identity, engage customers, and drive growth.
That said, not every business needs a full-time web developer. Many small and medium-sized companies leverage content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Wix, or AST Services CMS to design, manage, and optimize their websites efficiently — without extensive coding knowledge.
These platforms empower teams to launch professional websites quickly while keeping development costs manageable, ensuring businesses of all sizes can maintain a strong digital presence.
Web Development vs. Web Programming
At first glance, web development and web programming may seem identical — and while they are closely related, there’s an important distinction between the two. Understanding this difference helps clarify the unique roles and skills involved in building modern websites and web applications.
What Is Web Development?
Web development refers to the complete process of creating and maintaining websites or web applications. It covers everything from design and structure to coding, content integration, and performance optimization.
Web development involves using various programming languages, tools, and frameworks to turn an idea into a fully functional website. It also includes broader responsibilities such as:
-
Planning and managing website projects
-
Coordinating with designers, content creators, and stakeholders
-
Ensuring responsive design and user experience
-
Managing website updates and security
In short, a web developer oversees the entire lifecycle of a website — from concept to completion — ensuring that both technical performance and user experience meet the desired goals.
What Is Web Programming?
Web programming, on the other hand, focuses specifically on the coding and scripting side of a website. It’s the technical backbone that powers functionality, interactivity, and data processing.
A web programmer writes code that makes a website dynamic — handling data, processing user input, integrating APIs, and managing databases. Unlike web developers who may oversee the full project, web programmers typically specialize in particular areas such as:
-
Building and testing specific website features
-
Writing scripts for automation or user interactions
-
Debugging and troubleshooting functionality issues
-
Managing server-side or client-side logic
Simply put, web programming is a core part of web development, but not the entirety of it. While web developers often take a broader, multidisciplinary approach, web programmers concentrate on the logic and functionality that make a site work behind the scenes.
Why the Difference Matters
Recognizing the difference between web development and web programming helps businesses and professionals better understand project requirements and roles.
-
Web development focuses on the big picture — planning, designing, coding, testing, and launching the website.
-
Web programming zeroes in on the technical execution — writing the code that brings interactivity and functionality to life.
Both are essential. Together, they create the seamless online experiences that define today’s digital world.
 Web Development Basics
Web Development Basics
- What is a website?
- What is an IP address?
- What does HTTP mean?
- What is coding?
- What does front-end mean?
- What does back-end mean?
- What is a CMS?
- What is cybersecurity?
1. What Is a Website?
A website is a collection of digital files — such as text, images, videos, and code — that are stored on special computers called servers. These servers “host” websites, meaning they store the files and make them accessible to users across the internet.
When you type a web address (like www.example.com) into your browser, your computer sends a request to the server where the website is hosted. The server then responds by sending the necessary files back to your browser, allowing the site to load on your screen.
Your browser (such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Firefox, or Safari) is the program that interprets and displays these files so you can interact with the website. The device you use to access a site — whether it’s a computer, phone, or tablet — is known as a client.
In simple terms:
-
Server = where the website lives
-
Browser = the tool that displays the website
-
Client = the device you use to visit the website
Together, they form the foundation of how the web works.
2. What Is an IP Address?
Every device and website connected to the internet has a unique digital identifier called an IP address (Internet Protocol address).
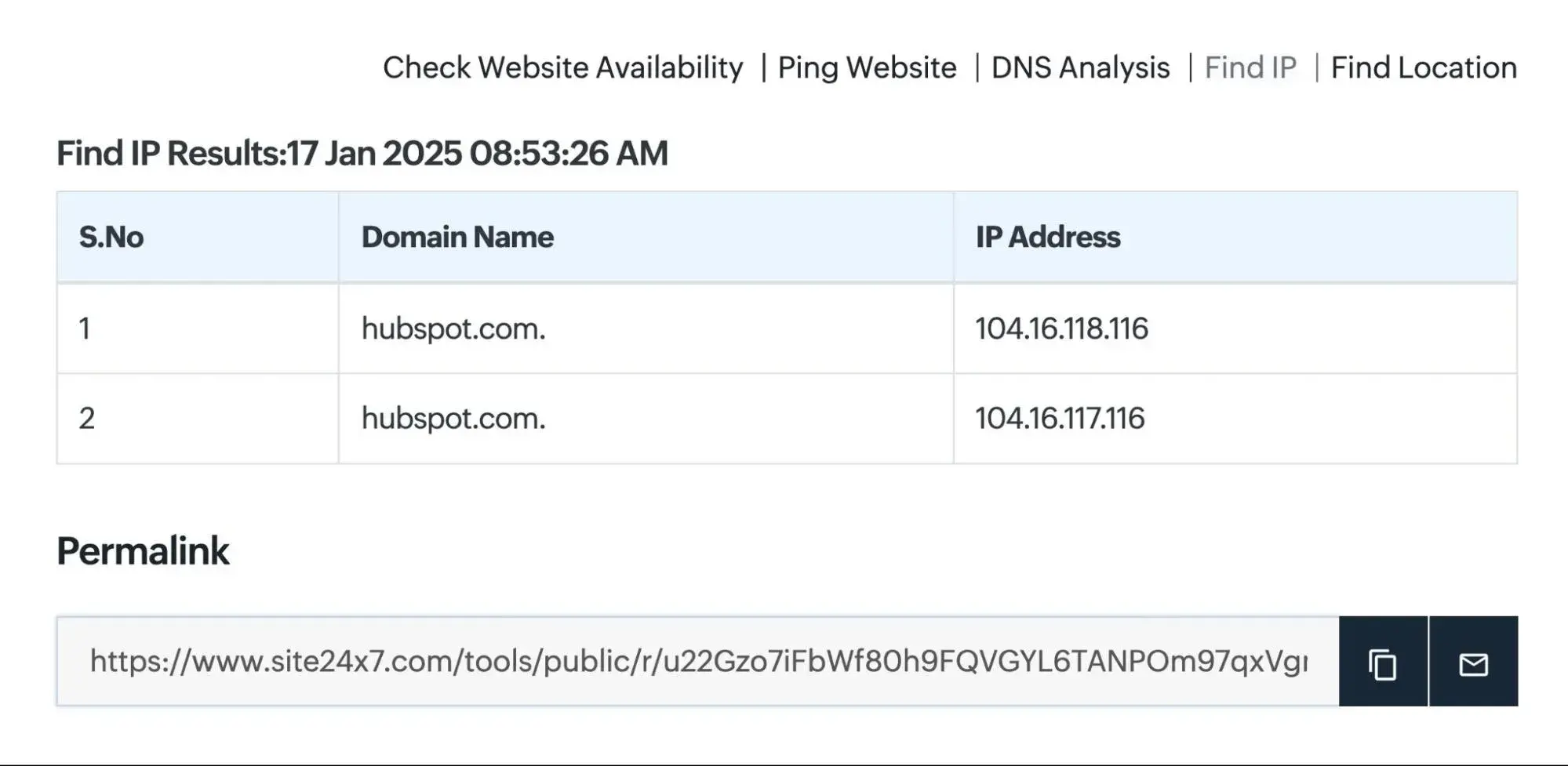
An IP address is a series of numbers (for example, 104.16.118.116) that allows computers to find and communicate with each other over the internet — much like a street address helps identify a specific house in a city.
When you visit a website, your browser uses the site’s domain name (like astservices.com) to locate its IP address. This lookup process happens automatically through the Domain Name System (DNS), which acts as the internet’s phonebook — matching human-friendly domain names to their numerical IP addresses.
If you’re curious, you can find any website’s IP address by:
-
Using tools like Site24x7 or WhatIsMyIPAddress.com, or
-
Running a Traceroute via Command Prompt (Windows) or Network Utility (Mac).
In short, an IP address ensures that the right data reaches the right destination — making smooth communication across billions of devices possible.
3. What Is a Domain Name?
If this concept feels new, that’s completely normal — because you’ve likely been using domain names every day without realizing it.
A domain name is the easy-to-remember address you type into your browser to visit a website — for example, www.google.com or www.astservices.com. While every website technically lives at a numerical IP address, domain names make it much easier for users to find and access sites without remembering long strings of numbers.
Behind the scenes, domain names are connected to their respective IP addresses through a system known as the Domain Name System (DNS).
Think of DNS as the internet’s phonebook — it translates human-friendly domain names into the IP addresses that computers use to locate and load websites.
If you’re planning to become a web developer, it’s important to understand how DNS works, since it plays a crucial role in how websites are found and accessed online.
💡 Pro Tip: You can find your device’s IP address simply by typing “what’s my IP address” into your web browser’s search bar.
4. What Does HTTP Mean?
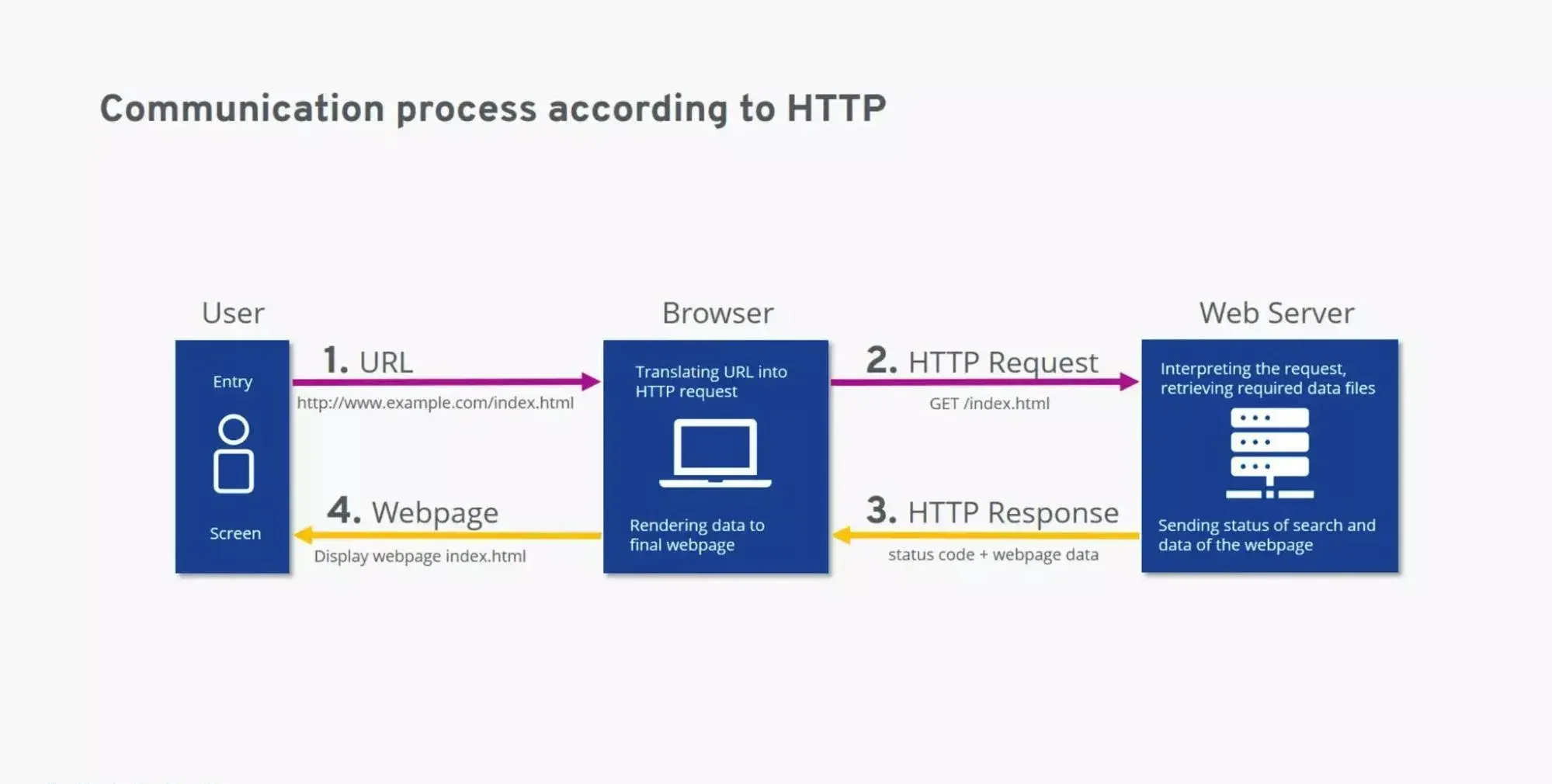
HTTP, short for HyperText Transfer Protocol, is the communication system that connects your computer (the client) to the server where a website’s data is stored.
In simpler terms, HTTP defines how data and messages are sent and received across the web. It’s the set of rules that ensures browsers and servers “speak the same language” when exchanging information.
Here’s how it works:
-
When you type a website URL into your browser or click a link, your computer sends an HTTP request to the website’s server.
-
The server responds by sending back the necessary data — HTML, images, scripts, and more — in an HTTP response.
-
Your browser then interprets that data and displays it as a fully rendered web page.
You can think of HTTP as a translator between you and the internet — it takes your request for a webpage, retrieves the necessary files, and presents them in a format you can easily understand.
For aspiring web developers, especially those focusing on back-end development, understanding HTTP is essential. It forms the foundation of how data travels between users and servers, making it one of the most important concepts in modern web development.
4. What Is Coding?
Coding is the process of writing instructions for computers, servers, or applications using programming languages. These languages are called “languages” because, like human languages, they have their own vocabulary, syntax, and grammar rules that computers can interpret.
Each line of code serves as a command that tells a computer what to do — from displaying a button to processing a payment or running an app. Every piece of software, website, and mobile app is written in at least one programming language.
Programming languages can vary depending on the platform, operating system, and project requirements. Generally, coding languages fall into two main categories:
-
Front-end (client-side) — what users see and interact with.
-
Back-end (server-side) — what happens behind the scenes to power the application.
💡 Pro Tip: When a company advertises for a Full Stack Developer, they’re looking for someone skilled in both front-end and back-end development — a versatile professional capable of building an entire web solution from start to finish.
5. What Does Front-End Mean?
The front-end, also known as the client-side, is everything you see and interact with when visiting a website or using a web application. It includes layouts, colors, text, images, buttons, forms, animations, and navigation menus — all of which are built using front-end coding languages.
Common front-end technologies include:
-
HTML (HyperText Markup Language): structures web content.
-
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): styles and formats that content.
-
JavaScript: adds interactivity and dynamic functionality.
Front-end development ensures that websites are responsive, user-friendly, and visually engaging, allowing users to play videos, expand images, highlight text, or fill out forms — all without constantly communicating with the web server.
6. What Does Back-End Mean?
The back-end, or server-side, is the part of a website or application that users don’t see directly. It’s the engine that processes data, runs business logic, and communicates with databases to ensure everything works properly on the front-end.
While the front-end handles what users see, the back-end manages how things actually function. For example, when you log into a website, it’s the back-end that verifies your credentials and retrieves your user data.
Popular back-end programming languages include:
-
Python
-
PHP
-
Java
-
Ruby
-
C#
-
Node.js (JavaScript runtime)
There are typically more back-end languages than front-end ones, as servers can be configured to run a variety of technologies depending on performance and scalability needs.
7. What Is a CMS (Content Management System)?
A Content Management System (CMS) is a web application that allows users to create, edit, organize, and publish digital content — often without needing to write any code.
Unlike website builders such as Wix or Squarespace, a CMS offers greater flexibility and scalability, making it ideal for managing complex websites, blogs, or online stores.
Some of the most popular CMS platforms include:
-
WordPress — ideal for blogs and business websites.
-
Drupal — suited for enterprise-level projects.
-
Joomla — a flexible, open-source CMS for various use cases.
-
Shopify / Magento — designed for e-commerce management.
A CMS empowers teams to manage website content more efficiently while developers focus on custom design, functionality, and integrations.
8. What Is Cybersecurity?
In today’s digital world, cybersecurity plays a crucial role in protecting websites, data, and online systems from malicious attacks. Hackers and cybercriminals are constantly developing new ways to exploit vulnerabilities — aiming to steal sensitive data, disrupt website operations, or even crash entire servers.
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of securing networks, systems, and digital assets against these threats. It involves implementing strategies, technologies, and best practices to safeguard both businesses and users from unauthorized access or data breaches.
Common cybersecurity measures include:
-
Firewalls and encryption protocols
-
SSL certificates to secure website connections
-
Regular software updates and patch management
-
Data backup and recovery systems
-
User authentication and strong password policies
Because cyber threats evolve constantly, regular security audits are essential. These audits help identify vulnerabilities before attackers do, ensuring your website remains safe and your users’ trust stays intact.
At AST Services, we believe that understanding cybersecurity fundamentals is a vital part of web development. A secure website not only protects your business data but also enhances your brand credibility and user confidence.
 Types of Web Development
Types of Web Development
- Front-End Development
- Back-End Development
- Full Stack Development
- Website Development
- Desktop Development
- Mobile Development
- Game Development
- Embedded Development
- Security Development
Exploring the Different Types of Web Development
My journey into web development began in the dynamic world of front-end design, where creativity meets technology. I was fascinated by how lines of code could transform into visually appealing, interactive web experiences that engage users.
As I advanced, I delved into back-end development, discovering the complex systems and logic that power websites behind the scenes. Learning languages like Python and Ruby gave me a deep appreciation for how both the front-end and back-end work together to deliver seamless digital experiences.
Whether you’re planning to hire a web developer or become one, it’s essential to understand the different types of web development — each representing a unique aspect of how websites and web applications are built.
While these areas often overlap, most developers specialize in one or more of the following disciplines:
1. Front-End Development
Front-end developers focus on the client-facing side of websites — everything users see and interact with directly. This includes the layout, color schemes, typography, navigation menus, animations, and overall user interface (UI).
Their goal is to create visually engaging and user-friendly designs that make the web experience smooth and intuitive. Front-end developers use languages and tools such as:
-
HTML – for structuring content
-
CSS – for styling and layout
-
JavaScript – for interactivity and dynamic features
They also often work closely on user experience (UX), ensuring that every visual and interactive element helps users achieve their goals efficiently.
2. Back-End Development
While front-end developers manage what users see, back-end developers handle what they don’t — the server-side of websites and web applications.
They ensure that every feature, form submission, and piece of data runs smoothly behind the scenes. Back-end developers work with systems such as:
-
Servers and databases (e.g., MySQL, MongoDB)
-
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
-
Programming languages like Python, PHP, Ruby, Java, and C#
Their responsibilities include managing website functionality, data security, content structure, and performance optimization. Back-end developers often collaborate closely with front-end teams to connect the user interface with server-side logic.

3. Full Stack Development
Full Stack Developers are proficient in both front-end and back-end development, enabling them to build complete websites, web applications, or software solutions from start to finish.
The term “stack” refers to the combination of technologies that work together to power a website — from the server and database (back end) to the interface users interact with (front end).
Because of their versatile expertise, full stack developers are highly sought after by organizations that need professionals capable of managing every stage of the development process. Their broad skill set allows them to:
-
Optimize overall site and app performance.
-
Identify and fix issues before they escalate.
-
Guide other team members across different development areas.
To become a full stack developer, one must gain hands-on experience and in-depth knowledge across multiple technologies — often through a comprehensive full stack development course or real-world practice.
4. Website Development
Website Developers specialize in creating fully functional websites. They may focus on front-end, back-end, or full stack development, but their primary goal is to design and develop responsive, secure, and engaging websites that meet user and business needs.
Unlike mobile app or software developers, website developers work specifically with web technologies such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, and CMS platforms like WordPress. Their work ensures that businesses maintain a strong online presence and deliver seamless user experiences across all devices.
5. Desktop Development
Desktop Developers create software applications that run locally on a user’s computer, rather than through a web browser. Examples include productivity tools, accounting software, and offline design programs.
While desktop applications run independently, there’s often an overlap with web development — especially when an app needs both offline and online functionality. These developers typically work with languages such as C++, C#, Java, or Python.
6. Mobile Development
Mobile Developers specialize in building apps for smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices. These apps are designed to deliver smooth, responsive, and intuitive experiences optimized for smaller screens and touch interfaces.
Mobile development requires knowledge of specialized languages and frameworks, such as:
-
Swift and Objective-C for iOS (Apple)
-
Kotlin and Java for Android
-
Flutter and React Native for cross-platform apps
Even if you’re not developing a mobile app, it’s essential to make your website mobile-friendly to reach the growing number of users who browse primarily on mobile devices.
7. Game Development
Game Developers focus on building interactive, visually rich, and immersive digital games. They work across various platforms — including consoles (PlayStation, Xbox), PC, and mobile.
This field combines creativity with technical expertise, using languages and engines like C++, C#, Unity, and Unreal Engine. Since many games today are played online or have mobile versions, game development often overlaps with web and mobile development.
8. Embedded Development
Embedded Developers work on programming hardware devices that aren’t traditional computers — such as smart appliances, IoT devices, wearables, and real-time systems.
With the rise of smart technology and the Internet of Things (IoT), embedded development has become a rapidly growing field. These developers typically use languages like C, C++, or Python to create efficient, lightweight software that runs directly on hardware.
9. Security Development
Security Developers (often known as ethical hackers) specialize in building systems that protect websites and applications from cyber threats. They simulate real-world attacks to identify weaknesses before malicious hackers can exploit them.
Their responsibilities include:
-
Conducting vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
-
Implementing data encryption and security protocols.
-
Developing tools to monitor and prevent breaches.
Security developers play a vital role in maintaining data integrity, privacy, and user trust, ensuring digital assets remain safe from evolving threats.
Front-End Web Development Languages
Front-end web development focuses on building the visual and interactive elements of a website — the part users see and engage with. It’s often the most accessible starting point for newcomers entering the web development field.
Here are the core languages every front-end developer should master:
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
HTML is the foundation of every website. It defines the structure and content of web pages, including text, headings, images, and links. Developers use HTML to create the layout and organize information before adding design and interactivity.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
If HTML forms the skeleton, CSS provides the style. It defines the visual presentation of a website — including colors, fonts, layouts, and spacing. CSS also allows developers to make websites responsive, ensuring they look great on any device.
Developers often use frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS to streamline the styling process and maintain design consistency.
JavaScript
JavaScript brings websites to life. It enables interactivity — from dynamic menus and sliders to pop-ups and animations. JavaScript runs directly in the user’s browser, improving real-time functionality and enhancing the user experience.
Popular JavaScript frameworks and libraries like React, Vue.js, and jQuery make it easier to build modern, dynamic interfaces efficiently.
Together, these three technologies — HTML, CSS, and JavaScript — form the foundation of every successful website.
Front-End Web Development Roadmap
If you’re ready to begin your journey into front-end development, here’s a simple roadmap to follow:
-
Understand how websites work.
Learn the fundamentals of how data moves online, including:-
How devices communicate over the internet.
-
The difference between HTTP and HTTPS.
-
How domain names and the DNS system function.
-
How browsers render web pages.
-
What APIs and the Document Object Model (DOM) are.
-
-
Learn HTML to create basic web pages.
Start by mastering HTML to build structured, readable content. Once you’re comfortable, experiment with styling it using CSS and adding functionality with JavaScript. -
Explore beginner-friendly resources.
Platforms like Codecademy, freeCodeCamp, and W3Schools offer excellent courses and projects to strengthen your understanding. -
Build and practice continuously.
The best way to learn is by creating — start with small projects like personal portfolios, landing pages, or simple web apps.
Use CSS to Style Your Web Page
While HTML forms the foundation of your website, CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) gives it life and visual appeal. CSS controls how your website looks — from colors and typography to spacing, alignment, and responsive layouts.
In front-end web development, CSS is one of the most essential languages to master. It allows you to transform basic HTML structures into visually engaging and modern web pages that enhance the user experience.
To get started, explore beginner-friendly resources such as:
-
The Ultimate Guide to CSS
-
Tutorials on classes and selectors
-
Understanding the box model
-
Learning Flexbox for responsive layouts
You can also take Codecademy’s free CSS course, which complements their HTML course perfectly and helps you grasp the core concepts quickly.
As you progress, using CSS frameworks can help streamline your workflow and maintain design consistency. Popular options like Bootstrap and Tailwind CSS allow you to build responsive layouts faster, saving time while improving quality.
Add Interactivity with JavaScript
Once you’re comfortable with HTML and CSS, it’s time to make your website interactive. That’s where JavaScript (JS) comes in.
JavaScript enables dynamic functionality — allowing you to create animations, dropdown menus, sliders, form validations, and interactive buttons that engage users.
You can start with Codecademy’s free JavaScript course, which introduces you to the basics of:
-
Variables and data types
-
Conditionals and loops
-
Functions and scope
-
Arrays and objects
Mastering JavaScript is key to building more engaging and responsive websites that feel modern and alive.
Deploy Your Website
After building your first website using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, the next step is to make it accessible to the world — by deploying it online.
If your site doesn’t rely on back-end functionality (like databases or APIs), you can use static hosting services. A great free option is Cloudflare Pages, though there are many alternatives such as:
-
Netlify
-
GitHub Pages
-
Vercel
Simply upload your static files (HTML, CSS, JS), connect your domain name, and your website will be live for anyone to visit. Congratulations — you’ve officially launched your first working website!
Expand Your Knowledge
Once you’ve mastered the front-end basics, it’s time to level up your skills. Expanding your expertise will make you a more versatile and in-demand developer.
Here are a few directions to continue your learning journey:
-
Explore advanced JavaScript and CSS libraries like React, Vue, or Tailwind CSS.
-
Learn Git and version control to manage and collaborate on code efficiently.
-
Understand back-end development to create more advanced, data-driven applications.
-
Experiment with CMS platforms such as WordPress, Webflow, or CMS to streamline website management.
Each new skill adds another layer of depth to your development career — helping you build more powerful, scalable, and professional web solutions.
Back-End Web Development Languages
While front-end developers focus on what users see, back-end developers work behind the scenes to ensure websites function seamlessly. They handle databases, servers, and application logic, enabling all the user-facing features to work properly.
Back-end development is often considered more challenging, as it requires understanding how servers, APIs, and databases interact with each other. Here are some of the most widely used back-end programming languages:
Python
Python is a powerful yet beginner-friendly language known for its simplicity and readability. It’s widely used for back-end development, automation, and data processing.
Python offers several frameworks that make web development easier, such as:
-
Django — a robust, high-level framework ideal for building scalable web applications.
-
Flask — a lightweight, flexible framework suited for smaller projects or microservices.
Thanks to its vast ecosystem of libraries and tools, Python remains one of the most popular languages for back-end developers worldwide.
Popular Back-End Development Languages
While front-end development focuses on what users see and interact with, back-end development powers the unseen functionality that keeps websites running smoothly.
Back-end developers work with databases, servers, and APIs — ensuring every button click or form submission works exactly as it should.
Below are some of the most important and in-demand back-end programming languages used by developers today.
Python
In addition to back-end development, Python offers a wide range of other use cases — from automation and data analysis to artificial intelligence and machine learning. This versatility makes Python one of the most valuable and adaptable languages to learn.
Python’s simplicity and readability make it ideal for beginners, while powerful frameworks like Django and Flask allow developers to build scalable and secure web applications efficiently.
PHP
PHP is a widely used server-side scripting language designed specifically for web development. It integrates seamlessly with HTML and offers strong features for managing databases, generating dynamic web content, and handling user interactions.
Frameworks such as Laravel and Symfony help developers create secure, maintainable, and high-performance web applications.
Additionally, WordPress — the world’s most popular content management system — is built on PHP, making it an excellent choice if you plan to develop or customize WordPress-based websites.
Ruby
Ruby is a dynamic, object-oriented programming language that emphasizes simplicity, readability, and productivity. It’s best known for the Ruby on Rails framework, which provides a powerful structure for developing robust and scalable web applications quickly.
Ruby’s elegant syntax and large ecosystem of libraries make it a popular choice for startups and developers who value rapid development without sacrificing flexibility.
Java
Java is one of the most versatile and widely adopted programming languages, prized for its performance, stability, and scalability.
It’s a top choice for building enterprise-level applications that require strong security and reliability.
Frameworks like Spring and Hibernate streamline complex development processes, enabling developers to build powerful, database-driven systems efficiently.
Thanks to its platform independence, Java runs on virtually any operating system, making it a long-standing favorite in enterprise web development.
C# (C-Sharp)
Developed by Microsoft, C# is a modern, general-purpose programming language widely used for building Windows applications, web services, and enterprise software.
With the support of the .NET framework, C# allows developers to create secure, scalable, and high-performance back-end systems.
It’s an excellent choice for businesses using Microsoft technologies and for developers building applications across Windows and cloud environments.
Node.js
Node.js isn’t a programming language but a JavaScript runtime environment built on Chrome’s V8 engine. It allows developers to run JavaScript on the server side, making full-stack JavaScript development possible.
With its event-driven, non-blocking architecture, Node.js excels at handling large volumes of concurrent connections — making it perfect for real-time applications, chat apps, and APIs.
Its scalability and efficiency have made it a top choice among modern web developers and startups worldwide.
Back-End Web Development Roadmap
Back-end development is the backbone of any website or web application — it’s what ensures everything runs smoothly behind the scenes.
To become a skilled back-end developer, you need a mix of technical knowledge, problem-solving skills, and a deep understanding of how the web works.
While it’s often considered more complex than front-end development, it’s absolutely learnable with the right roadmap. Let’s explore the step-by-step process to get started in back-end web development.
1. Understand How the Internet Works
Before diving into coding, it’s crucial to understand how the internet functions at a fundamental level.
Knowing how different systems communicate helps you troubleshoot, optimize, and design smarter back-end solutions.
Here are some key concepts to learn:
-
How devices communicate on the internet
-
What HTTP and HTTPS are, and how they work
-
How domain names and the Domain Name System (DNS) function
-
How web browsers process requests and responses
-
What APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are and how they enable systems to interact
You’ll revisit these concepts many times as you progress, but having a strong foundation early on will make your learning journey much smoother.
2. Choose a Back-End Language and Framework
Once you have a grasp of the basics, it’s time to pick your first back-end programming language.
There are many to choose from — Python, PHP, Java, Ruby, C#, and JavaScript (Node.js) are some of the most popular options.
Each language has its strengths, so choose one that aligns with your career goals:
-
PHP + Laravel → Ideal for WordPress and traditional web projects
-
Python + Django or Flask → Great for modern web apps and startups
-
JavaScript + Node.js → Perfect for full-stack JavaScript development
-
Java + Spring → Excellent for enterprise-level applications
-
C# + .NET → Best for Windows-based or enterprise systems
Start with one language, master it, and then expand your skill set over time.
3. Learn Version Control and Repo Hosting
Version control is an essential skill for every developer — especially back-end developers working on complex systems or collaborating in teams.
Git is the most widely used version control system. It helps you:
-
Track changes to your code
-
Revert to previous versions
-
Collaborate seamlessly with other developers
Once you’ve learned Git, use platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket to host your repositories and manage your projects effectively.
4. Learn About Databases
No back-end project is complete without a database to store and manage data.
Understanding how databases work — and how to integrate them with your back-end — is a key part of becoming a proficient developer.
There are two main types of databases to learn:
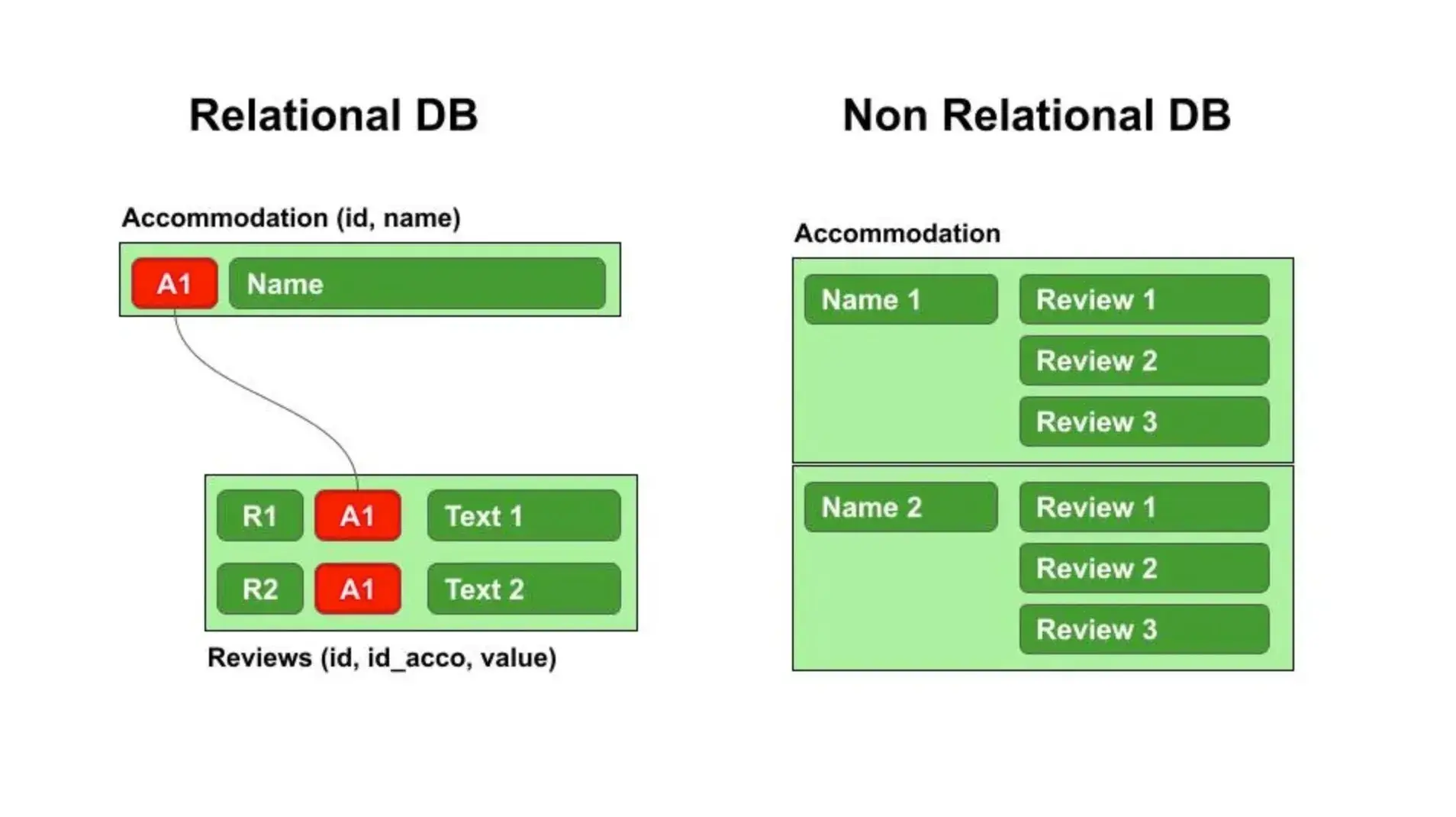
Relational Databases (SQL)
These databases organize data into tables with predefined relationships.
Examples include:
-
MySQL
-
PostgreSQL
-
SQLite
Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL)
These databases are more flexible and store data in document or key-value formats.
Examples include:
-
MongoDB
-
Redis
Both SQL and NoSQL databases are valuable to learn — SQL for structured data and complex queries, and NoSQL for scalability and real-time applications.
5. Understand Server Management and Deployment
Once your code and database are ready, you’ll need to host them on a server so users can access your website or application.
Learn the fundamentals of:
-
Web servers (like Apache, Nginx, or Node.js servers)
-
Cloud hosting platforms (AWS, DigitalOcean, Google Cloud, etc.)
-
APIs and RESTful services
-
Deployment pipelines using tools like Docker or CI/CD
This knowledge helps you ensure your back-end is not only functional but also secure, scalable, and easy to maintain.
6. Prioritize Security and Performance
Security is one of the most important aspects of back-end development.
You’ll need to understand how to:
-
Encrypt sensitive data
-
Prevent SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS)
-
Implement authentication and authorization securely
-
Conduct regular security audits
Strong security practices protect your website, your users, and your reputation.
Continue Learning: Advanced Back-End Development Concepts
Once you’re comfortable with the basics of back-end web development, it’s time to level up. The following topics will help you build secure, efficient, and scalable applications that can handle real-world demands.
1. Start with Relational Databases
When you’re just beginning your back-end development journey, it’s best to start with relational databases.
These databases use structured schemas with tables, rows, and columns — making them ideal for learning how data relationships work.
Unless your project specifically requires a non-relational approach, relational databases are a great default choice.
💡 Pro Tip: Learn SQL (Structured Query Language) — it’s the foundation for interacting with most relational databases. With SQL, you’ll be able to:
-
Query and retrieve specific data from tables
-
Create and modify database structures
-
Manage relationships between data efficiently
Once you’re comfortable with relational databases, you can expand into non-relational (NoSQL) databases such as MongoDB or Redis.
Each has its strengths depending on the project’s scalability and flexibility requirements.
2. Learn About APIs
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are what connect the back end to the front end — they make your web applications functional, interactive, and dynamic.
By learning APIs, you’ll understand how to send data from your server to users’ browsers or mobile apps.
Here are key concepts and technologies to explore:
-
REST (Representational State Transfer) — the most common architecture for APIs
-
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) — a lightweight format for exchanging data
-
GraphQL — a modern alternative to REST for more efficient data fetching
-
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) — a legacy protocol still used in enterprise systems
-
gRPC — a high-performance framework for communication between services
-
Webhooks — automated event notifications between systems
-
WebSockets — for real-time, two-way communication (e.g., chat apps, live dashboards)
Understanding these technologies will allow you to connect databases, handle requests, and build powerful, data-driven applications.
3. Learn How Security Works
Security is non-negotiable in back-end web development. As your applications grow, protecting them from vulnerabilities becomes more complex — and more important.
Here are some key areas to study:
-
Password hashing (MD5, SHA, bcrypt, scrypt, etc.)
-
HTTPS and SSL/TLS for encrypted data transfer
-
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) configuration
-
Server security fundamentals (firewalls, access control, etc.)
-
Content Security Policy (CSP) for browser-side protection
-
User authentication and authorization methods
Learning these principles will help you create secure, stable applications that protect both your users and your system.
4. Understand Testing and Quality Assurance
Before deploying any website or web app, you need to ensure it works as intended. That’s where testing comes in.
Here are the main types of tests every back-end developer should know:
-
Unit Testing: Testing individual functions or modules in isolation
-
Integration Testing: Ensuring different components work well together
-
Functional Testing: Checking if the system meets all functional requirements
By learning these testing methods, you’ll save yourself — and your clients — from costly errors later on.
5. Learn How to Deploy Your Web Applications
Once your application is fully developed and tested, it’s time to deploy it — making it live for users worldwide.
At this stage, you should learn about:
-
Containerization & Virtualization: Using tools like Docker or Kubernetes to streamline deployment
-
Web Servers: Understanding how Apache, Nginx, and Node.js servers handle requests
-
Cloud Platforms: Working with AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure for scalability and reliability
-
Continuous Integration/Deployment (CI/CD): Automating your deployment process for smoother updates
Deploying your projects marks the transition from developer to professional engineer — it’s when your code starts impacting real users.
6. Focus on Performance and Scalability
Once your project is deployed, your job isn’t done — it’s just beginning.
The next challenge is optimizing performance, improving scalability, and preparing for future growth.
Here are a few areas to explore:
-
Caching (Redis, Varnish) for faster response times
-
Database indexing for optimized queries
-
Load balancing for distributing traffic efficiently
-
Microservices architecture for modular, scalable applications
The more you learn about scalability, the better equipped you’ll be to build large, enterprise-level applications.
The Website Development Process
Early in my web development journey, I used to jump into projects without a clear roadmap — and the result was often chaos.
It felt like trying to assemble a puzzle without knowing what the final picture should look like.
Everything changed when I started working on a complex eCommerce project. It demanded a balance of front-end design and back-end architecture, and I quickly learned the value of a structured process.
A solid web development process turns complex projects into manageable, step-by-step journeys. It keeps your team aligned, ensures high-quality results, and saves time in the long run.
Here’s a breakdown of the key stages in a successful website development process that I’ve found most valuable:
✅ 1. Planning & Requirement Gathering – Understand the client’s goals, target audience, and technical requirements.
✅ 2. Wireframing & Design – Create the visual blueprint of the website.
✅ 3. Front-End Development – Code the design using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
✅ 4. Back-End Development – Build the server, database, and APIs to power the site.
✅ 5. Testing & Quality Assurance – Debug, test functionality, and ensure compatibility.
✅ 6. Deployment – Host the website on a live server.
✅ 7. Maintenance & Updates – Monitor performance and roll out improvements.
1. Form a Plan
Before writing a single line of code or sketching your first design, it’s crucial to start with a strategic plan. This stage lays the foundation for your entire website development process, ensuring every decision aligns with your business objectives and audience needs.
The first step is collaboration — connect with your web development, marketing, and financial teams to clearly define your goals, target audience, and available resources. This alignment helps you avoid confusion later and sets the project up for success.
Here are a few essential questions to guide your planning phase:
-
What is the main goal of your website? (e.g., generate leads, sell products, share information)
-
Who is your target audience, and what actions do you want them to take on your website?
-
What type of website are you creating — an informational site, eCommerce platform, or membership portal?
-
What kind of content will you publish, and how frequently?
-
How will you structure your website for optimal navigation and user experience?
-
What is your budget and expected timeline for completion?
Taking the time to answer these questions early ensures clarity and direction for everyone involved.
Simply put, a well-defined roadmap at the beginning saves time, money, and frustration later. It’s also important to maintain open communication with your team throughout the process to ensure alignment, consistency, and collaboration from start to finish.
2. Create a Wireframe
Every successful website begins with a clear visual plan — a wireframe. This acts as the architectural blueprint of your website, outlining the structure, layout, and placement of elements before any coding begins.
A wireframe helps you visualize how users will interact with your site and ensures that key pages, such as the homepage, product pages, or service listings, are strategically positioned for maximum engagement.
You don’t need advanced design software to create one — even a rough sketch on paper can do the job. However, digital tools like Figma, Adobe XD, Slickplan, or MindNode make collaboration smoother and adjustments easier.
By building a strong wireframe, you’ll avoid design inconsistencies and ensure every page has a clear purpose in your user journey.

3. Draft the Website Layout and Design
Once the wireframe is approved, it’s time to bring your vision to life. The design phase focuses on UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) — creating a visually appealing and easy-to-navigate site that aligns with your brand identity.
This step involves selecting:
-
Color palettes and typography
-
Image styles and iconography
-
Layout spacing and grid systems
-
Buttons, menus, and other interactive elements
For businesses, consistency is key. Every visual component should reflect your brand’s tone and purpose — whether it’s corporate professionalism, creative energy, or modern simplicity.
4. Develop the Front-End
After finalizing the design, developers transform your static mockup into an interactive interface using front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
This phase focuses on what users actually see and interact with — animations, forms, navigation, and responsive layouts that adapt to all devices. Frameworks like React, Vue.js, or Bootstrap are often used to speed up the process and maintain design consistency.
5. Develop the Back-End
The back-end is where the magic happens behind the scenes. It’s responsible for powering your website’s functionality, managing databases, handling user authentication, and connecting everything to the front-end.
Developers work with languages such as PHP, Python, Java, or Node.js, along with frameworks like Laravel, Django, or Express.js. They also integrate APIs and configure databases (like MySQL or MongoDB) to ensure data flows smoothly across the system.
6. Integrate Content and Functionality
With the structure ready, it’s time to add real content — text, images, videos, and downloadable resources. If the site uses a CMS (Content Management System) like WordPress or Drupal, content integration becomes simpler for non-developers to manage later on.
At this stage, developers also integrate contact forms, search functionality, eCommerce features, or booking systems, depending on the site’s goals.
7. Test, Review, and Optimize
Before launch, rigorous testing ensures that your site performs flawlessly across browsers and devices. This includes:
-
Functional testing: Ensuring links, buttons, and forms work as intended
-
Performance testing: Checking load times and responsiveness
-
Security testing: Protecting user data and preventing vulnerabilities
-
SEO testing: Ensuring metadata, URLs, and structure are search-engine-friendly
User feedback is also valuable here — it helps you identify usability issues before your site goes live.
8. Launch the Website
Once the testing phase is complete, it’s time to make your site live. This includes finalizing the hosting setup, domain configuration, and deployment. A soft launch (internal testing) is often done before the official public release to ensure a seamless user experience.
9. Maintain and Update Regularly
Website development doesn’t end after launch. Continuous maintenance ensures your site stays fast, secure, and up to date. This includes regular updates, security patches, backups, and content optimization to keep your digital presence strong.
Website Development Resources
One of the most valuable lessons I’ve learned in my web development journey is that continuous learning is essential. The web is always evolving — new frameworks, tools, and technologies emerge constantly — and staying ahead means committing to ongoing education.
When I encountered challenges with complex coding problems, I discovered just how many incredible online resources exist to help developers learn, grow, and solve problems. From free tutorials to in-depth professional courses, there’s something for every skill level.
Below are some excellent resources you can explore to strengthen your understanding of web development and enhance your skills.
Web Development Courses and Classes
Whether you’re interested in front-end, back-end, or full stack development, countless platforms provide accessible, high-quality learning materials. Here are a few trusted resources that many developers — including professionals at AST Services — recommend:
1. HubSpot Website Blog
The HubSpot Website Blog is a must-read for both beginners and experienced developers. It offers clear, actionable insights that simplify the complexities of coding and website creation. From expert tips and tutorials to trend analyses and course recommendations, the HubSpot blog keeps you informed about the ever-evolving digital landscape.
2. TutorialsPoint
TutorialsPoint is a comprehensive, free learning hub for aspiring developers. It features tutorials, eBooks, and video lessons covering a wide range of web development topics — including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, Python, and more. The platform’s structured approach makes it easy to progress step by step and build a strong foundation in coding.
Dive Into Web Development
Stepping into the world of web development has been a true turning point for me. This field isn’t just about learning to code — it’s about transforming the way people interact with the digital world. Every line of code you write contributes to shaping how users connect, engage, and experience the internet.
Here’s the truth: whether you’re looking to elevate your business presence online or create the next groundbreaking web application, understanding web development is absolutely essential. The field is dynamic, fast-paced, and constantly evolving — offering endless opportunities for creativity, innovation, and growth.
At AST Services, we believe that web development is more than a skill — it’s a gateway to the future. Every project we take on reflects our passion for technology, design, and functionality. And trust me, in this ever-changing digital era, there’s never a dull moment in web development.







No comment